- Research
Modeling, Simulation, and Implementation of Solar-Driven Water Splitting Devices
Xiang, C. et al. Modeling, Simulation, and Implementation of Solar-Driven Water-Splitting Devices. Angewandte Chemie, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201510463 (2016).
JCAP researchers led the effort and produced a critical review article on modeling and simulation guided research and development of integrated solar-driven water-splitting cells.
This provides an excellent reference for researchers working with solar water-splitting devices.
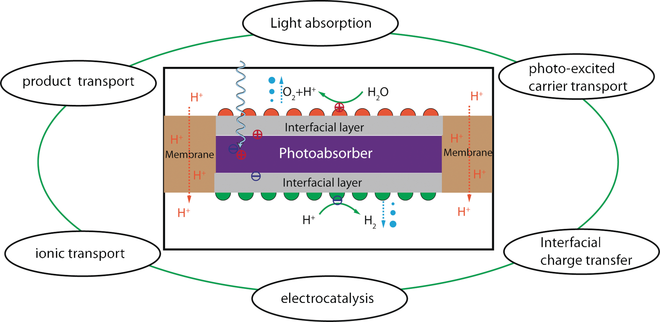
The review details capture and transport of light in the semiconductor, electrocatalysis, ion transport in the membrane and aqueous electrolytes, transport of product gas, and describesmulticomponent interactions between these physicochemical phenomena.
The article also critical reviewed a range of unique prototype designs including water-vapor systems, solar concentrator couple PEC systems, macroscopic planar systems, micro-structured PEC systems and particle-based PEC systems.
Reprinted from Xiang, C. et al. Modeling, Simulation, and Implementation of Solar-Driven Water-Splitting Devices. Angewandte Chemie, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201510463 (2016)..
Schematic illustration of various coupled photoelectrochemical processes in an integrated solar-driven water-splitting cell
Contact: azweber@lbl.gov cxx@caltech.edu